DeePMD-kit v3 Official Release: Multi-Backend Support, DPA-2 Large Model, and Plugin Mechanism
1. Multi-backend framework: Powered by TensorFlow, PyTorch, and JAX

DeePMD-kit v3 implements a flexible and pluggable backend framework, providing a consistent training and inference experience across multiple backends. Version 3.0.0 includes the following backends:
- TensorFlow Backend: Static graph for efficient computation.
- PyTorch Backend: Dynamic graph, simplifying model extension and development.
- DP Backend: Reference backend implemented with NumPy and Array API.
- JAX Backend: Static graph + JIT, based on the DP backend and Array API.
| Function | TensorFlow | PyTorch | JAX | DP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local frame descriptor | ✅ | |||
| se_e2_a descriptor | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| se_e2_r descriptor | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| se_e3 descriptor | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| se_e3_tebd descriptor | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| DPA-1 descriptor | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| DPA-2 descriptor | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Hybrid descriptor | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Fit energy | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Fit dipole | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Fit polar | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Fit DOS | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Fit properties | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| ZBL | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| DPLR | ✅ | |||
| DPRc | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Spin | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Ladder calculation | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Model training | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| Model compression | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| Python inference | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| C++ inference | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
The main features of the multi-backend framework include:
- Models can be trained using the same training data and input scripts across different backends, allowing users to switch backends based on efficiency or convenience requirements.
1 | # Training a model using the TensorFlow backend |
- Use
dp convert-backendto convert models between different backends. It supports backend-specific file extensions (e.g., TensorFlow uses.pb, PyTorch uses.pth).
1 | # Convert a TensorFlow model to a PyTorch model |
- Inference with different backends can be performed using the
dp testinterface, Python/C++/C interfaces, or third-party packages such asdpdata, ASE, LAMMPS, AMBER, Gromacs, i-PI, CP2K, OpenMM, ABACUS, and others.
1 | # In LAMMPS file: |
- Adding new backends to DeePMD-kit has become faster and more streamlined.
DP-GEN has also released a new version, v0.13.0, which supports DeePMD-kit’s multi-backend functionality through thetrain_backendparameter (can be set totensorfloworpytorch).
2. DPA-2 Model: A General Large-Atom Model for Molecular and Material Simulations
The DPA-2 model provides a robust architecture for large-atom models (link), enabling highly accurate representation of various chemical systems for high-quality simulations. In version 3.0.0, DPA-2 supports single-task or multi-task training on the PyTorch backend and inference using the JAX backend.
The DPA-2 descriptor consists of two modules: repinit and repformer, as shown in the figure below.
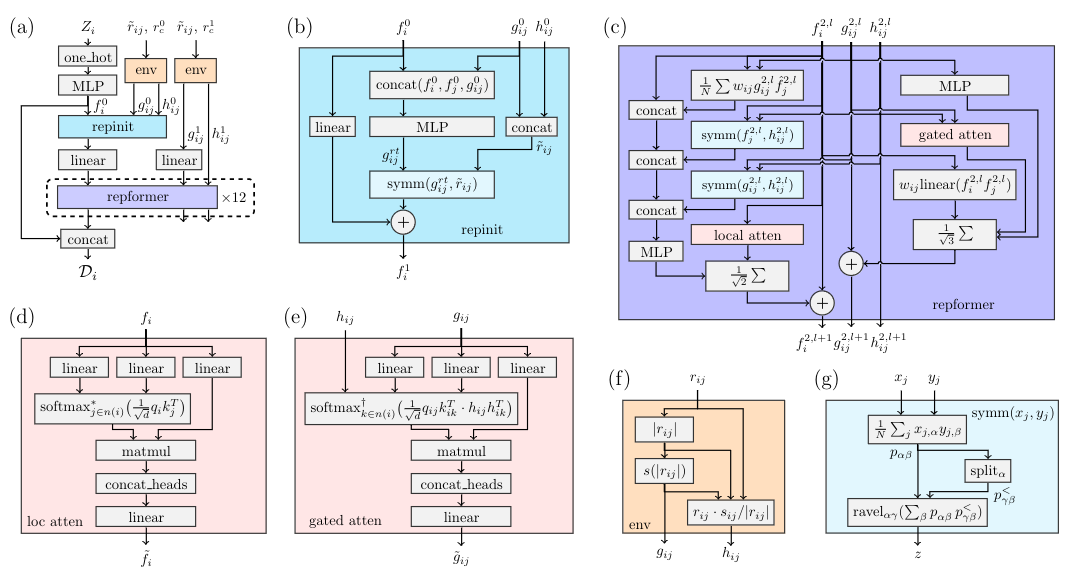
The PyTorch backend supports training strategies required for large-atom models, including:
- Parallel Training: Train large-atom models across multiple GPUs to improve efficiency.
1 | torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 --no-python dp --pt train input.json |
- Multi-task Training: Share descriptors across diverse datasets computed using different DFT methods to train large-atom models.
- Fine-tuning: Train pre-trained large-atom models on smaller, task-specific datasets. The PyTorch backend supports the
--finetuneparameter in thedp --pt traincommand line.
3. Plugin Mechanism: Connecting DeePMD-kit with External Models
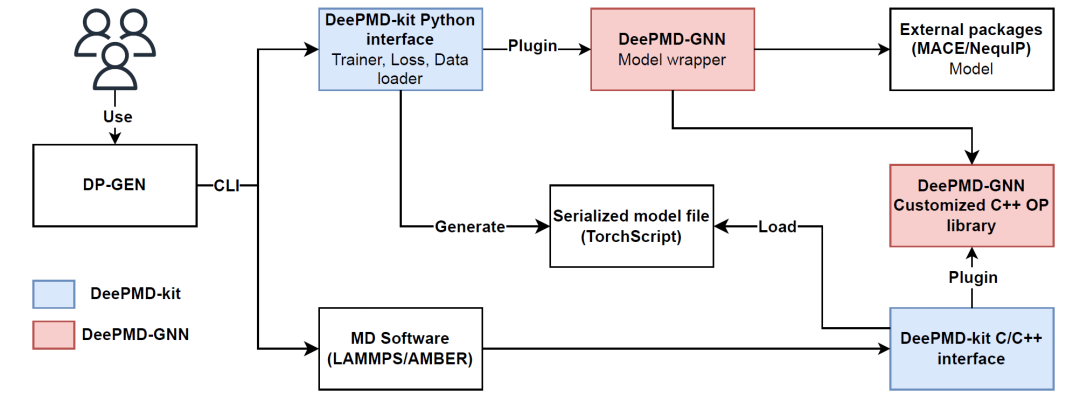
Version 3.0.0 significantly enhances the plugin mechanism, enabling the development or integration of potential energy models using TensorFlow, PyTorch, or JAX frameworks. This allows users to leverage DeePMD-kit's training modules, loss functions, and various interfaces.
Here is an example of a plugin package: deepmd-gnn. The deepmd-gnn plugin supports training MACE and NequIP models within DeePMD-kit using familiar dp commands.
1 | # after installing deepmd-gnn |
4. More functions
Descriptor se_e3_tebd
- A descriptor designed for fitting arbitrary properties of a system.
New Training Parameters:
- max_ckpt_keep: Specifies the maximum number of checkpoints to keep.
- change_bias_after_training: Allows adjustment of biases after training.
- stat_file: Provides a file for recording statistical information during training.
New Command-Line Interfaces:
dp change-bias: Modify model biases post-training.dp show: Display model details or parameters.
Enhanced JSON Input File Support in VSCode:
- View parameter documentation directly in JSON input files.
- Check parameters for correctness within VSCode.
Support for Latest LAMMPS Version:
- Compatible with stable_29Aug2024_update1.
The PyTorch backend for DeePMD-kit was initially developed in the deepmd-pytorch project and was later fully migrated to the deepmd-kit project.
5. Contributors to the deepmd-pytorch Project:
Chenqqian Zhang, Chun Cai, Duo Zhang, Guolin Ke, Han Wang, Hangrui Bi, Jinzhe Zeng, Junhan Chang, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaochen Shi, Yifan Li, Yiming Du, Zhaohan Ding, Xuejian Qin, Xinzijian Liu
Contributors to the deepmd-kit Project (after branching out for v3 development):
Anyang Peng, Chenqqian Zhang, Chenxing Luo, Chun Cai, Duo Zhang, Han Wang, Jia-Xin Zhu, Jinzhe Zeng, Pinghui Mo, Ruosong Shi, Sensen He, Sigbjørn Løland Bore, Xiangyu Zhang, Yan Wang, Yifan Li, Yiming Du, Yong-Bin Zhuang, Yunpei Liu, Zhangmancang Xu, Zhe Deng, Zhengtao Huang, Zhenyu Wang
We would also like to thank everyone who participated in testing and bug reporting over the past eight months.
Version Release Notes & Offline Package Download:
https://github.com/deepmodeling/deepmd-kit/releases/tag/v3.0.0
Documentation:
https://docs.deepmodeling.com/projects/deepmd/en/v3.0.0/
6. Join the Team of Jinzhe Zeng!
The author of this article and one of the main contributors to DeePMD-kit, Jinzhe Zeng, earned a bachelor's degree in Chemistry from East China Normal University in July 2019. He is expected to receive his Ph.D. in Chemistry from Rutgers University in January 2025. Afterward, he will join the School of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science at the University of Science and Technology of China (working in Suzhou) as a tenure-track associate professor and will establish his own research team.
The team will welcome outstanding undergraduate students to apply for graduate positions. One of the research directions will focus on the development of DeePMD-kit.
Contact: jinzhe.zeng@rutgers.edu